Overview
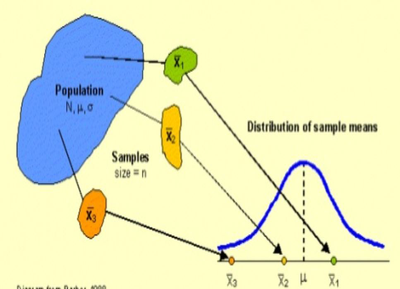
When we want information about the population proportion of successes, we often take a simple random sample and use the sample proportion to estimate the unknown parameter . The sampling distribution of the sample proportion describes how the statistic varies in all possible samples of the same size from the population. In this lesson, students will explore the shape and variability of this distribution, and learn how to evaluate claims using the sampling distribution.
Underlying Pages
-
0. Student Directions -
Preview as Student
-
1. Thinking about our Context -
Preview as Student
-
2. Introducing our Context -
Preview as Student
-
3. Apply - evaluate claims using the sampling distribution -
Preview as Student
-
4. Introduction to sampling from 2 populations -
Preview as Student
-
5. Setting up for 2 samples -
Preview as Student
-
6. Carrying out the 2 Samples and calculating the difference in sample proportions -
Preview as Student
-
7. Formulas and Calculations -
Preview as Student
-
8. Reminder about the need to collect and analyze statistics -
Preview as Student
-
9. Practice with 2 proportions -
Preview as Student
Standards
Computational Thinking in STEM 2.0
- Computational Data Practices
- Computational Modeling and Simulation Practices
